Branchenmeldungen 10.06.2015
Literaturhinweise: Was wir über künstlichen Zahnschmelz wissen
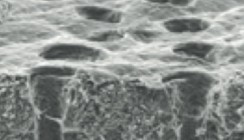
Der Remineralisierungseffekt von
Carbonat-Hydroxylapatit-Kristallen auf Dentin
The Remineralizing Effect of Carbonate-Hydroxyapatite
Nanocrystals on Dentine
L. Rimondi, B. Palazzo, M. Lafisco, L. Canegallo, F.
Demarosi, M. Merlo, N. Roveri | Materials Science Forum, 2007, Vols.
539–543:602–605
Synthetische biomimetische
Carbonat-Hydroxylapatit-Kristalle zur Remineralisation von Zahnschmelzoberflächen
Synthetic biomimetic
carbonate-hydroxyapatite nanocrystals for enamel remineralization
L. Rimondi, C. L. Bianchi, E. Foresti, M. Iafisco, B.
Palazzo, G. Capelletti, N. Roveri | Advanced Materials Research, 2008, Vols.
47-50:821-824
Hydroxylapatit kann Zahnschmelz
reparieren/Zahnerosion verhindern/Bildung bakterieller Plaque
erschweren
Prof. Dr. med. dent. M.
Hannig, Universitatsklinikum des Saarlandes, Klinik für Zahnerhaltung,
Parodontologie und Präventive Zahnheilkunde
NanoMed 2009 –
Nanomaterials in Dentistry –
Neo-Mineralisation der
Zahnschmelzoberfläche: Unterschiedliche Effekte von zahnschmelzähnlichen
Hydroxylapatit-Kristallen und Fluoridionen
Surface Enamel
Remineralization: Biomimetic Apatite Nanocrystals and Fluoride Ions Different
Effects
N. Roveri, E. Battistella, C. L. Bianchi, I. Foltran,
E. Foresti, M. Iafisco, M. Lelli, A. Naldoni, B. Palazzo, L. Rimondini
Journal of Nanomaterials Volume 2009 (2009), Article
ID 746383
Randomisierte Doppelblind-Studie
zum Vergleich der desensibilisierenden Wirkung einer neuen Zahncreme auf Basis
von Carbonat-Hydroxylapatit-Kristallen und einer natriumfluorid-/
kaliumnitrat-haltigen Zahncreme
A double-blind randomized-controlled trial comparing
the desensitizing efficacy of a new dentifrice containing carbonate/hydroxyapatite
nanocrystals and a sodium fluoride/potassium nitrate dentifrice
G. Orsini, M. Procaccini, L. Manzoli, F. Giuliodori,
A. Lorenzini, A. PutignanoJournal of Clinical Periodontology (June 2010) Volume
37, Issue 6: 510–517
Signifikante Reduktion der
Schmerzempfindlichkeit hypersensibler Zähne
Quelle: IADR/AADR/CADR 89th General Session, 2011, San
Diego, Calif.
Remineralisierung
bei initialer Karies
Enamel and dentine remineralization by
nano-hydroxyapatite toothpastes
P. Tschoppe, D. L. Zandim, P. Martus, A. M. Kielbassa
Journal of Dentistry
(Juni 2011), 39(6): 430-7
Natürliche Zahnschmelzabnutzung –
eine physiologische Quelle von Hydroxylapatit-Partikeln für die Regulierung des Biofilms
und die Zahnreparatur?
Natural enamel wear – A physiological source of
hydroxylapatite nanoparticles for biofilm Management and tooth repair?
C. Hannig, M. Hannig | Medical Hypotheses (April 2010)
Volume 74, Issue 4: 670-672
Antibakterielle Effekte ohne
Eingriff in das ökologische Gleichgewicht der Mundhöhle
Influence of a mouthwash containing hydroxyapatite
microclusters on bacterial adherence in situ
C. Hannig, S. Basche, T.
Burghardt, A. Al-Ahmad, M. Hannig
Clinical Oral Investigations (April 2013), Volume 17,
Issue 3: 805-814
Wirksamkeit einer neuen Zahncreme
mit Carbonat-Hydroxylapatit-Kristallen auf Plaque- und Gingiva-Indices bei
Patienten mit leichter Parodontitis
Efficacy of a new carbonate/hydroxyapatite
microcrystal dentifrice on plaque and gingival indices in mild periodontitis
patients
I.
Harks, Y. Jokel-Schneider, U. Schlagenhauf, T. May, M. Gravemeier, K. Prior, B.
Ehmke under revision of J clin oral Investigations.